A brief introduction of “Fibulin-3 as a Blood and Effusion Biomarker for Pleural Mesothelioma”
Pleural mesothelioma is the tumor that originated in the peritoneal mesothelial cell. Pleural mesothelioma is related with asbestos exposure. There are significant differences in the incidence of pleural mesothelioma in different countries, this is mainly related to the asbestos consumption of these countries over the past several decades. The mortality rate of pleural mesothelioma has a rising tendency in recent years.
The common first symptom of pleural mesothelioma is chest pain, cough and shortness of breath. There are also symptoms of fever, sweating or joint pain. Most patients have a lot of pleural effusion and short of breath, the patients that without mass of pleural effusion will have the symptomatic of chest pain.
Pleural effusion can be found by the chest X-ray, at the same time, you will find that the lungs are covered by tumor tissue. CT examination are most useful for patients who may have malignant pleural mesothelioma. Although advances in radiation therapy, chemotherapy, and surgical management for malignant pleural mesothelioma, the survival time of malignant pleural mesothelioma patients is extended, the survival time remains about only one year. Thus, the early diagnosis of pleural mesothelioma is necessary.
Dr Harvey I. Pass and the research team of New York university Langone medical center have published an article in the New England journal of medicine, the paper title is: “Fibulin-3 as a Blood and Effusion Biomarker for Pleural Mesothelioma”.
The researchers have used ELISA kit (SEF422Hu) to detect the plasma fibulin-3 levels in patients with malignant pleural mesothelioma, asbestos-exposed persons without cancer, patients with effusions not due to mesothelioma and healthy controls. The result showed that plasma fibulin-3 levels were significantly higher in patients with pleural mesothelioma than in other groups. The result is shown in figure 1.
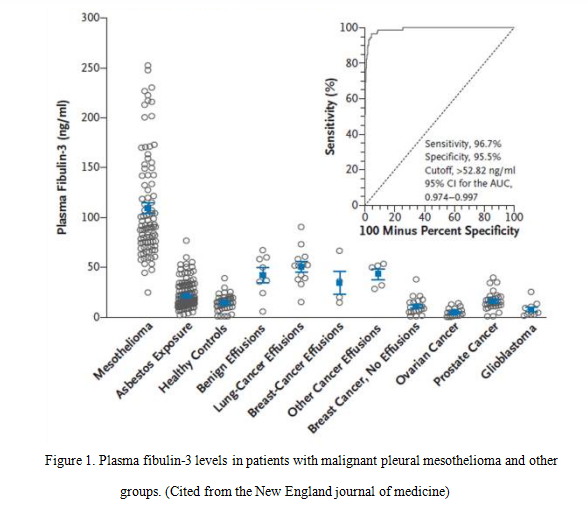
Secondly, the researchers have used our company’s ELISA kit (SEF422Hu) to detect the effusion fibulin-3 levels in patients with mesothelioma and patients with effusions not due to mesothelioma. The result showed that effusion fibulin-3 levels were significantly higher in patients with mesothelioma than in patients with effusions not due to mesothelioma. The result is shown in figure 2.
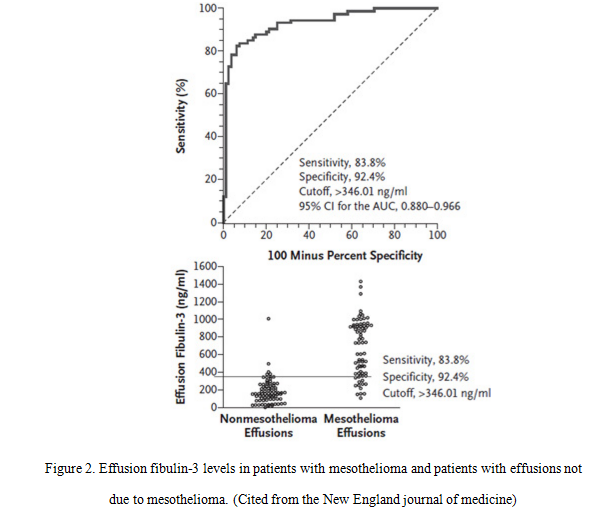
It can be concluded that the concentration of fibulin-3 in plasma can distinguish healthy people with exposure to asbestos from patients with mesothelioma by ELISA, combined with analysis of the concentration of fibulin-3 in effusion and plasma can further differentiate mesothelioma effusions from other effusions by ELISA. The concentration of Fibulin-3 in blood and effusion can be used as biomarker for pleural mesothelioma.
