Efficacy of serum apelin and galectin-3 as potential predictors of mortality in severe COVID-19 patients

On January 12, 2023, Erdal İn, Department of Chest Diseases, Malatya Turgut Özal University Faculty of Medicine, Turkey, and his team published a paper titled “Efficacy of serum apelin and galectin-3 as potential predictors of mortality in severe COVID-19 patients” in Journal of Medical Virology. Their research shows that galectin-3 may be a simple, useful, and prognostic biomarker that can be utilized to predict patients at high risk of mortality in severe COVID-19 patients.

The kits [ELISA Kit for Apelin (APLN), CED066Hu; ELISA Kit for Galectin 3 (GAL3), SEA303Hu] of Cloud-Clone brand was chosed in this article, we are so proud for supporting the reaserchers.

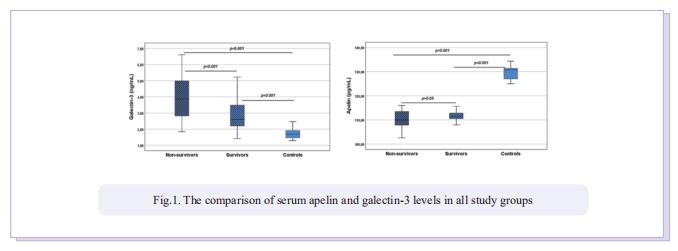
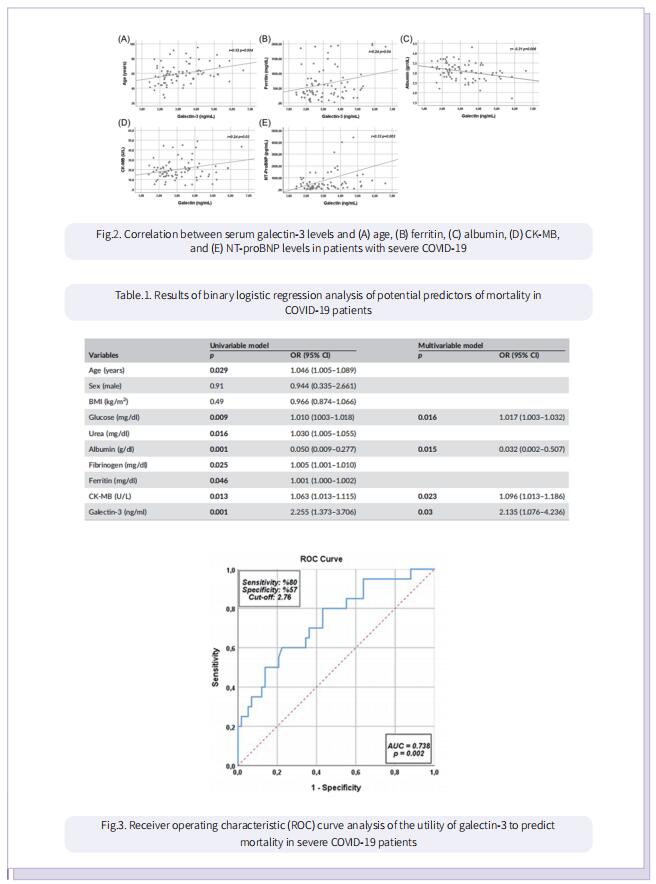
Apelin is a cardioprotective biomarker while galectin‐3 is a pro‐inflammatory and profibrotic biomarker. Endothelial dysfunction, hyperinflammation, and pulmonary fibrosis are key mechanisms that contribute to the development of adverse outcomes in Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID‐19) infection. This study aims to analyze the prognostic value of serum apelin and galectin‐3 levels to early predict patients at high risk of mortality in patients hospitalized for severe COVID‐19 pneumonia. The study included 78 severe COVID‐19 patients and 40 healthy controls. The COVID‐19 patients were divided into two groups, survivors and nonsurvivors, according to their in‐hospital mortality status. Basic demographic and clinical data of all patients were collected, and blood samples were taken before treatment. In our study, serum apelin levels were determined to be significantly lower in both nonsurvivor and survivor COVID‐19 patients compared to the control subjects (for both groups, p < 0.001). However, serum apelin levels were similar in survivor and nonsurvivor COVID‐19 patients (p > 0.05). Serum galectin‐3 levels were determined to be higher in a statistically significant way in nonsurvivors compared to survivors and controls (for both groups; p < 0.001). Additionally, serum galectin‐3 levels were significantly higher in the survivor patients compared to the control subjects (p < 0.001). Positive correlations were observed between galectin‐3 and age, ferritin, CK‐MB and NT‐proBNP variables (r = 0.32, p = 0.004; r = 0.24, p = 0.04; r = 0.24, p = 0.03; and r = 0.33, p = 0.003, respectively) while a negative correlation was observed between galectin‐3 and albumin (r = −0.31, p = 0.006). Multiple logistic regression analysis revealed that galectin‐3 was an independent predictor of mortality in COVID‐19 patients (odds ratio [OR] = 2.272, 95% confidence interval [CI] = 1.106–4.667; p = 0.025). When the threshold value for galectin‐3 was regarded as 2.8 ng/ml, it was discovered to predict mortality with 80% sensitivity and 57% specificity (area under the curve = 0.738, 95% CI = 0.611–0.866, p = 0.002). Galectin‐3 might be a simple, useful, and prognostic biomarker that can be utilized to predict patients who are at high risk of mortality in severe COVID‐19 patients.