Hepatic HuR modulates lipid homeostasis in response to high-fat diet

On June 16, 2020, professor Zhongzhou Yang from model animal research center of Nanjing university co-authored with Wengong Wang from Peking university health science center published a paper titled Hepatic HuR modulates lipid homeostasis in response to high-fat diet on Nature communications.
The ELISA kit (APOE, SEA704Mu; APOB, SEC003Mu) of Cloud-Clone brand was chosed to determine the concentation of APOE and APOB in this article, we are so proud for supporting the reaserchers.


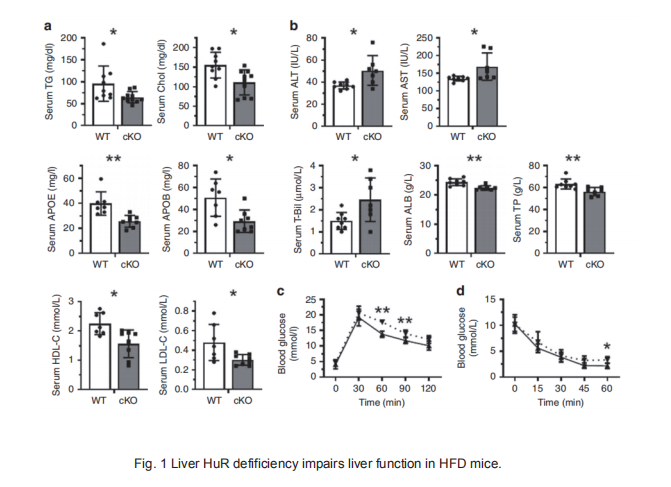
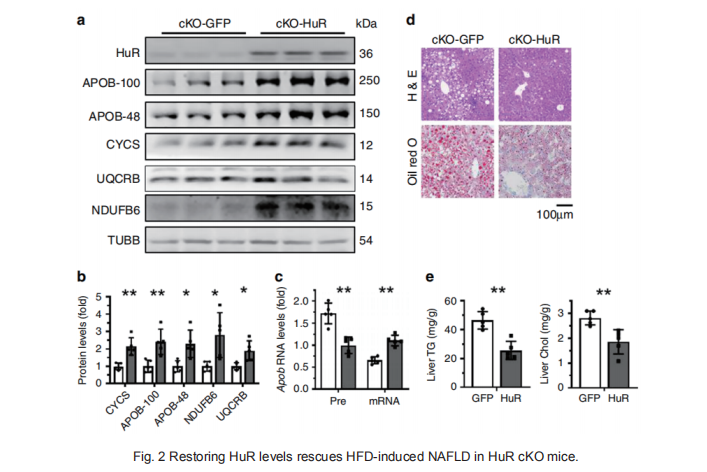
Lipid transport and ATP synthesis are critical for the progression of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD), but the underlying mechanisms are largely unknown. Here, we report that the RNA-binding protein HuR (ELAVL1) forms complexes with NAFLD-relevant transcripts. It associates with intron 24 of Apob pre-mRNA, with the 3′UTR of Uqcrb, and with the 5′UTR of Ndufb6 mRNA, thereby regulating the splicing of Apob mRNA and the translation of UQCRB and NDUFB6. Hepatocyte-specifific HuR knockout reduces the expression of APOB, UQCRB, and NDUFB6 in mice, reducing liver lipid transport and ATP synthesis, and aggravating high fat diet (HFD)-induced NAFLD. Adenovirus-mediated re-expression of HuR in hepatocytes rescues the effect of HuR knockout in HFD-induced NAFLD. Our fifindings highlight a critical role of HuR in regulating lipid transport and ATP synthesis.