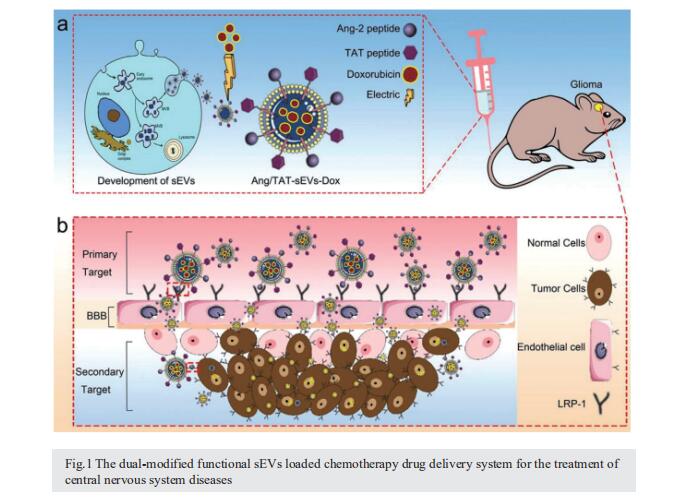
Specific anti-glioma targeted-delivery strategy of engineered small extracellular vesicles dual-functionalised by Angiopep-2 and TAT peptides

On August 6, 2022, Guosheng Cheng, School of Nano-Tech and Nano-Bionics, University of Science and Technology of China, China, and his team published a paper titled “Specific anti-glioma targeted-delivery strategy of engineered small extracellular vesicles dual-functionalised by Angiopep-2 and TAT peptides” in Journal of Extracellular Vesicles. They showed that utilization of the dualmodified small extracellular vesicles (sEVs) represents a unique and efficient strategy for drug delivery, holding great promise for the treatments of central nervous system diseases.

The kits [ELISA Kit for Creatine Kinase MB Isoenzyme (CKMB), SEA479Mu; ELISA Kit for Aspartate Aminotransferase (AST), SEB214Mu] of Cloud-Clone brand was chosed in this article, we are so proud for supporting the reaserchers.

Glioma is one of the primary malignant brain tumours in adults, with a poor prognosis. Pharmacological reagents targeting glioma are limited to achieve the desired therapeutic effect due to the presence of blood-brain barrier (BBB). Effectively crossing the BBB and specifically targeting to the brain tumour are the major challenge for the glioma treatments. Here, we demonstrate that the well-defined small extracellular vesicles (sEVs) with dual-targeting drug delivery and cell-penetrating functions, modified by Angiopep-2 and trans-activator of transcription peptides, enable efficient and specific chemotherapy for glioma. The high efficiency of engineered sEVs in targeting BBB and glioma was assessed in both monolayer culture cells and BBB model in vitro, respectively. The observed high targeting efficiency was re-validated in subcutaneous tumour and orthotopic glioma mice models. After loading the doxorubicin into dual-modified functional sEVs, this specific dual-targeting delivery system could cross the BBB, reach the glioma, and penetrate the tumour. Such a mode of drug delivery significantly improved more than 2-fold survival time of glioma mice with very few side effects. In conclusion, utilization of the dualmodified sEVs represents a unique and efficient strategy for drug delivery, holding great promise for the treatments of central nervous system diseases.