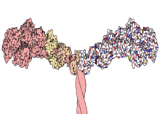
Myosinsare responsible for actin-based motility. The term was originally used to describe a group of similar ATPases found in striated and smooth muscle cells. Following the discovery by Pollard and Korn of enzymes with myosin-like function in Acanthamoeba castellanii, a large number of divergent myosin genes have been discovered throughout eukaryotes. Thus, although myosin was originally thought to be restricted to muscle cells, there is no single "myosin" but rather a huge superfamily of genes whose protein products share the basic properties of actin binding, ATP hydrolysis, and force transduction. Virtually all eukaryotic cells contain myosin isoforms. Some isoforms have specialized functions in certain cell types, while other isoforms are ubiquitous. The structure and function of myosin is strongly conserved across species, to the extent that rabbit muscle myosin II will bind to actin from an amoeba.
Organism species: Homo sapiens (Human)
| CATALOG NO. | PRODUCT NAME | APPLICATIONS | |
| Proteins | n/a | Complete Antigen of Myosin (Myo) | Antigenic Transformation Customized Service Offer |
| Antibodies | PAS098Hu01 | Polyclonal Antibody to Myosin (Myo) | WB; IHC; ICC; IP. |
| Assay Kits | SES098Hu | ELISA Kit for Myosin (Myo) | Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for Antigen Detection. |
