Mouse Model for Hepatic Ischemia (HI)
Hepatic ischemia/reperfusion; Liver ischemia
- Product No.DSI527Mu01
- Organism SpeciesMus musculus (Mouse) Same name, Different species.
- Prototype SpeciesHuman
- SourceHepatic Ischemia induced by Ischemia and reperfusion
- Model Animal StrainsBalb/c Mice(SPF), healthy, male, age: 6~8weeks, body weight:20g~25g.
- Modeling GroupingRandomly divided into six group: Control group, Model group, Positive drug group and Test drug group.
- Modeling Period4-6 weeks
- Modeling Method1 Mice were fasting and drinking freely 12h before surgery.
2. Anesthetized mice, lay the mice flat on the operating table, fixed their limbs, performed abdominal hair removal, and disinfected the operative area with iodine and 75% ethanol.
3. The abdominal cavity was opened 1cm from the abdominal midline incision, and the portal vein and hepatic artery supplied by the liver were carefully separated.
4. The portal vein and hepatic artery were clamped with a non-invasive vascular clip. 0.5min later, the occluded lobe was visibly white, indicating successful occlusion.The skin incision was clamped with hemostatic forceps to temporarily close the abdominal cavity, and the mice were placed on a 37℃ thermostatic heating pad to keep warm.
5. After 60 minutes of continuous ischemia, the abdominal cavity was reopened, and the vascular clamp was removed quickly to restore the blood flow of the ischemic liver. About 0.5 minutes, the liver in the ischemic area gradually recovered from white to bright red, indicating successful reperfusion.The abdominal muscle and skin were sutured layer by layer to close the abdominal cavity and the operation was completed.After the mice were awake, they were put back into the feeding room, and the status and survival of the mice were closely monitored and recorded. - ApplicationsDisease Model
- Downloadn/a
- UOM Each case
- FOB
US$ 200
For more details, please contact local distributors!
Model Evaluation
Hepatic ischemia injury score:
0 point: no hepatocyte injury
1 points: mild injury, characterized by vacuolation of cytoplasm and nuclear pyknosis of lesions
2 points: moderate injury, sinus dilation, vacuolation of cell solute, blurred cell boundary
3 points: moderate to severe injury, coagulated necrosis, massive sinusoidal swelling, exudation of red blood cells into the liver lock, increased eosinophilic cells, neutrophil peripheral (attached to the vascular wall)
4 points: severe necrosis, loss of liver structure, collapse of liver cord, hemorrhage, infiltration of neutrophils
Pathological Results
Left liver tissue 1.5cm×1cm×0.2cm was fixed in 4% paraformaldehyde solution for 24h, then dehydrated, embedded, paraffin section, HE staining, TUNEL staining.Necrosis was scored.Hepatic lobule structure was severely damaged, reticular fibrous scaffold collapsed, hepatic cell necrosis, vacuolar degeneration, hepatic cord and hepatic sinus hyperemia and swelling, with unclear boundary and inflammatory cell infiltration around.
Cytokines Level
Biochemical index detection:The levels of ALT (alanine aminotransferase), AST (aspartate aminotransferase), γ -glutamyltransferase (GGT), total bilirubin (T-Bil), direct bilirubin (D-Bil), indirect bilirubin (I-Bil), total bile acid (TBA) in serum of mice were detected at 0h, 3h, 6h, 12h, 24h and 72h after operation, respectively.
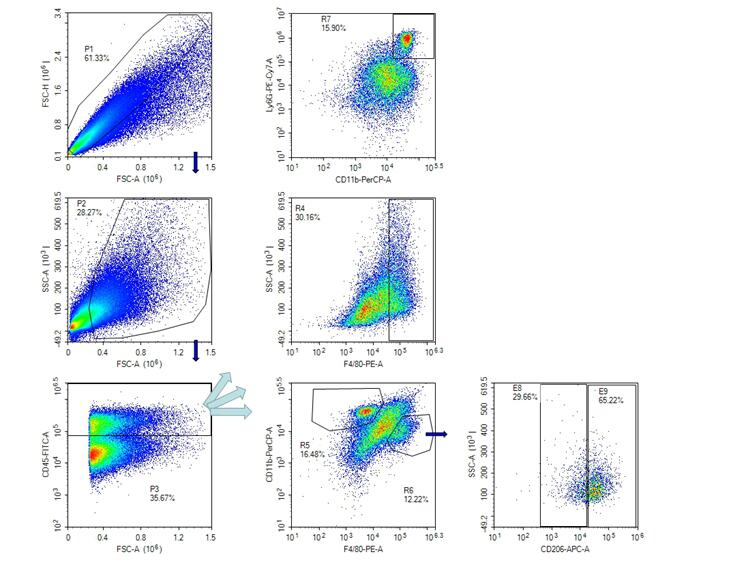
Flow detection:
1. Sample pre-processing
① Cut up: cut up the tissue in the digestive juice
② Add digestive fluid: add 5ml digestive fluid to each liver tissue
③ Digestion: digestion at 37℃ for 45min
④ Interruption: 1640 10ml of 10%FBS was added to the digested tissue to terminate the enzyme reaction.
⑤ Filtration: The tissue suspension is filtered through a 200-mesh filter
⑥ Washing: Single cell suspension was collected in a 50ml EP tube and centrifuged at 2000rpm for 10min.
⑦ Lamination: lamination with mouse lymphocyte separation solution
⑧cell collection: The transparent cell layer in the middle was absorbed, and the cells were centrifuged and washed once by FACs Buffer.
2. Flow dyeing:
①FcR blocking: Add 1% FcR blocker (Anti-CD16/32 antibody), 100ul per sample.
Incubated at 4℃ for 30min, and centrifuged by FACs Buffer.
② Sample surface antibody working fluid:
Mixed antibody working solution, 100ul per sample;
After adding the antibody working solution, the antibody was incubated at 4℃ and sheltered from light for 30min, and centrifuged by FACs Buffer.
PerCP anti-mouse CD11b
PE/Cy7 anti-mouse Ly-6G
FITC anti-mouse CD45
PE anti-mouse F4/80
3. Intracellular staining of samples:
Add 50ul of fixed broken film solution, and then gently blow and re-suspend with the tip of a gun. Keep out of light for 45min at room temperature.After completion, add 1x Perm /wash buffer for washing.
4. After staining, cells were suspended:
The samples were dyed (each sample was suspended using 200ul FACs Buffer), and stored at 4℃ away from light.
5. Flow loading machine:
The total number of samples was 500,000 per cell.
Statistical Analysis
SPSS software is used for statistical analysis, measurement data to mean ± standard deviation (x ±s), using t test and single factor analysis of variance for group comparison, P<0.05 indicates there was a significant difference, P<0.01 indicates there are very significant differences.
GIVEAWAYS
INCREMENT SERVICES
-
 Tissue/Sections Customized Service
Tissue/Sections Customized Service
-
 Serums Customized Service
Serums Customized Service
-
 Immunohistochemistry (IHC) Experiment Service
Immunohistochemistry (IHC) Experiment Service
-
 Small Animal In Vivo Imaging Experiment Service
Small Animal In Vivo Imaging Experiment Service
-
 Small Animal Micro CT Imaging Experiment Service
Small Animal Micro CT Imaging Experiment Service
-
 Small Animal MRI Imaging Experiment Service
Small Animal MRI Imaging Experiment Service
-
 Small Animal Ultrasound Imaging Experiment Service
Small Animal Ultrasound Imaging Experiment Service
-
 Transmission Electron Microscopy (TEM) Experiment Service
Transmission Electron Microscopy (TEM) Experiment Service
-
 Scanning Electron Microscope (SEM) Experiment Service
Scanning Electron Microscope (SEM) Experiment Service
-
 Learning and Memory Behavioral Experiment Service
Learning and Memory Behavioral Experiment Service
-
 Anxiety and Depression Behavioral Experiment Service
Anxiety and Depression Behavioral Experiment Service
-
 Drug Addiction Behavioral Experiment Service
Drug Addiction Behavioral Experiment Service
-
 Pain Behavioral Experiment Service
Pain Behavioral Experiment Service
-
 Neuropsychiatric Disorder Behavioral Experiment Service
Neuropsychiatric Disorder Behavioral Experiment Service
-
 Fatigue Behavioral Experiment Service
Fatigue Behavioral Experiment Service
-
 Nitric Oxide Assay Kit (A012)
Nitric Oxide Assay Kit (A012)
-
 Nitric Oxide Assay Kit (A013-2)
Nitric Oxide Assay Kit (A013-2)
-
 Total Anti-Oxidative Capability Assay Kit(A015-2)
Total Anti-Oxidative Capability Assay Kit(A015-2)
-
 Total Anti-Oxidative Capability Assay Kit (A015-1)
Total Anti-Oxidative Capability Assay Kit (A015-1)
-
 Superoxide Dismutase Assay Kit
Superoxide Dismutase Assay Kit
-
 Fructose Assay Kit (A085)
Fructose Assay Kit (A085)
-
 Citric Acid Assay Kit (A128 )
Citric Acid Assay Kit (A128 )
-
 Catalase Assay Kit
Catalase Assay Kit
-
 Malondialdehyde Assay Kit
Malondialdehyde Assay Kit
-
 Glutathione S-Transferase Assay Kit
Glutathione S-Transferase Assay Kit
-
 Microscale Reduced Glutathione assay kit
Microscale Reduced Glutathione assay kit
-
 Glutathione Reductase Activity Coefficient Assay Kit
Glutathione Reductase Activity Coefficient Assay Kit
-
 Angiotensin Converting Enzyme Kit
Angiotensin Converting Enzyme Kit
-
 Glutathione Peroxidase (GSH-PX) Assay Kit
Glutathione Peroxidase (GSH-PX) Assay Kit
-
 Cloud-Clone Multiplex assay kits
Cloud-Clone Multiplex assay kits
| Catalog No. | Related products for research use of Mus musculus (Mouse) Organism species | Applications (RESEARCH USE ONLY!) |
| DSI527Mu01 | Mouse Model for Hepatic Ischemia (HI) | Disease Model |
| TSI527Mu03 | Mouse Liver Tissue of Hepatic Ischemia (HI) | Paraffin slides for pathologic research: IHC,IF and HE,Masson and other stainings |